22 Apr
Global Clinical Trials take advantage of significant Australian R&D tax incentives

Australia and New Zealand are well-established regions for international clinical trials. Global sponsors understand the region’s ability to deliver quality research outcomes; rapid start-up, recruitment and participant retention, streamlined ethics and regulatory pathways, internationally accepted quality data from world-leading research facilities and Investigators. These key regional benefits are all delivered cost-effectively, with the added bonus of the attractive AU Government R&D Incentive, encouraging global companies to conduct research activities in Australia.
Clinical trials are high cost and high risk, so it makes sense to maximise the time and cost advantages of the Australian environment to deliver high quality, regulatory ready data.
Sponsors often struggle to understand the AU R&D Incentive program and an early understanding is important to ensure that appropriate structures and decisions are made. PharmaSols in conjunction with Acclime have developed a high-level summary of information new global biotech’s should consider when reviewing the AU R&D program.
AU R&D - A Quick Guide and Overview
The AU R&D incentive is one of many positive factors for conducting research in this region. Sponsors come to realise that the time savings delivered by this region often outweigh the AU R&D rebate $ value claimed.
“Other global regions can take 6-12 months longer in the start-up phase of a clinical trial. If you think about it, every day a clinical trial is delayed costs in terms of lost revenue. That cost is often more significant than any tax rebate.” - Nicole Elliott Strategy & Finance PharmaSols
“The AU R&D incentive is the cherry on the top of a sundae of reasons to conduct clinical trials in Australia.” – Liz Austin, Austin Legal
- Get early AU R&D Tax Advice
There are strict requirements that need to be met in order to claim the AU R&D tax incentive, so you’ll need to engage the experts from the outset – documentation is key.
- Understand key R&D terms
a. Aggregated Turnover: determines the rate
Most global biotech’s qualify in the under AUD$20m aggregated turnover category and therefore qualify for the 43.5% cash refund. This aggregated turnover revenue definition might include venture capital/investor/shareholder companies and this can push companies into the higher aggregated turnover category. This is often overlooked. Whilst your R&D spend may still qualify for the R&D tax incentive, in this case, it would come in the form of a tax offset (rather than a cash rebate)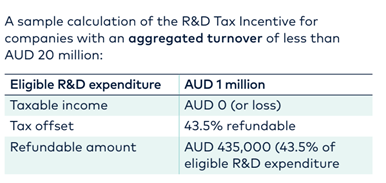
b. AU Eligible Entity: set up an AU Eligible entity before costs are incurred
For most global companies, this involves setting up a new AU entity and registering with the ATO/Dept of Industry. The incorporation of a new AU entity is a simple, inexpensive process that can normally be completed within 24-48hours. As only R&D costs incurred after registration of a company qualify, this is a vital first step that is often overlooked in the hurry to start up a new clinical trial.
c. Document your parent-subsidiary relationship
Your parent-AU subsidiary relationship will determine whether you are eligible to claim the R&D tax incentive and ultimately, the net value of the incentive. There are 2 primary relationships that provide access to the incentive: an ‘agency’ relationship or an ‘entrepreneurial’ relationship. Under an agency model, the AU entity is acting as an agent on behalf of the parent company. Under an entrepreneurial model, the AU entity is the major benefactor of the R&D and receives material beneficial interest in the results and a return on investment that an arm’s length entrepreneur would expect to receive for taking on the risk of conducting the trials. Regardless of the relationship you choose, you will need a legal agreement to evidence that your chosen relationship meets the requirements of the R&D tax incentive and complies with Australian transfer pricing principles.
“AU R&D Advisors, like Acclime, are an important part of the early stages of this R&D program. Often sponsors think it’s as simple as setting up a new AU registered company, but it is so much more complex than this. Get advice upfront and set up the appropriate structures right at the start.” - Nicole Elliott Strategy & Finance PharmaSols.
d. Eligible R&D activities: AU Govt recognises Phase 1-3 clinical trials
Phase 1, 2 and 3 clinical trials generally satisfy the R&D eligible activities definition. The AU govt has guidance and also recently released a determination noting that such trials should qualify for the R&D incentive.
Generally, only R&D activities conducted in AU qualify.
Overseas (ex Australia) R&D activities may qualify upon receipt of an Overseas Finding from the Dept of Industry. Applications for Overseas Findings need to be submitted in the year the overseas activities commence in order to claim the expense.
There are strict criteria for the grant of an Overseas Finding. Your application will need to establish that the overseas R&D activity(ies) meets the following conditions:
- overseas R&D has a significant scientific link to the AU R&D activities
- overseas R&D activity must be unable to be conducted in AU.This includes lack of access to facility, expertise, specific population or that equipment or activities contravene AU biosecurity laws. Generally speaking, cost is not an acceptable reason; and
- anticipated expenditure on all overseas R&D activities must be less than AU R&D activities
- there must be a core activity wholly undertaken in Australia.
Evidence is required as part of an application and an Overseas Finding application is made on a case-by-case basis. Overseas Findings cover expenditure in the year of application and 2 years following (for a total of 3 years).
Overseas Finding applications should be prepared by a tax advisor and the process can be expensive and time-consuming, with no guarantee of success. If your clinical trial requires critical ex Australia activities and you think those activities meet the above criteria, speak to a tax advisor for a preliminary view on your likelihood of success of an application for an Overseas Finding.
When do I claim? When do I get the cash rebate?
e. When do I claim? When do I get the cash rebate?
-
- Registered R&D activities with the Dept of Industry
- Income Tax Return submitted
- Refundable amounts are generally paid 6-10 weeks from the date of Income Tax Return lodgement.
The AU R&D Tax Incentive program supports Australia as an attractive region for global sponsors.
There is however potential for global sponsors to make critical errors when stepping through this complicated framework. Early advice from experts, like Acclime, is a good investment for every global sponsor who may be interested in conducting a clinical trial in this region with the support of the R&D tax incentive.
“PharmaSols are experts at delivering clinical trials. We know enough about the AU R&D program to know, that you need an AU R&D expert. It can be a simple process, but you need a good advisor.” - Nicole Elliott Strategy & Finance PharmaSols
Vital Steps:
- Talk with an R&D Advisor
- Confirm Eligible AU R&D Entity
- Get your legal documents in place to evidence entitlement to claim
- Review agreements with third-party suppliers (e.g., CROs) to identify any R&D tax incentive risks
- Register R&D activities with the Dept of Industry
- Review R&D expenditure and supporting documentation
ATO = Australian Tax OfficeDept of Industry = Department of Industry, Science, Energy and Resources, previously known as AusIndustry.
Find out more >>>R&D Fact Sheet
Contact >>> Acclime https://australia.acclime.com/conducting-rd/
Please note the above is general information and not formal R&D tax incentive and tax advice. We would strongly recommend formal advice be sought from a suitably qualified and experienced R&D advisor & tax advisor before conducting any R&D activities to ensure all of the requirements of the R&D tax incentive are met.
Other News
March 2024 (1)
February 2024 (1)
December 2023 (1)
November 2023 (1)
October 2023 (1)
September 2023 (2)
August 2023 (1)
July 2023 (1)
June 2023 (2)
May 2023 (3)
April 2023 (1)
March 2023 (2)
The Go-to region for clinical trials (1)
HiRO – our global advantage, tailored solutions and key partnerships (1) (1)
HiRO – an emerging full-service global CRO (1)
HiRO – Top CRO in APAC 2022 (1) (1)
November 2022 (1)
October 2022 (1)
September 2022 (1)
August 2022 (1)
July 2022 (1)
June 2022 (1)
May 2022 (1)
April 2022 (1)
March 2022 (1)
January 2022 (1)
December 2021 (1)
November 2021 (1)
October 2021 (2)
September 2021 (2)
August 2021 (3)
July 2021 (3)
June 2021 (2)
May 2021 (1)
April 2021 (2)
March 2021 (1)
February 2021 (1)
December 2020 (5)
November 2020 (1)
October 2020 (5)
September 2020 (1)
August 2020 (2)
May 2020 (5)
January 2024 (0)



